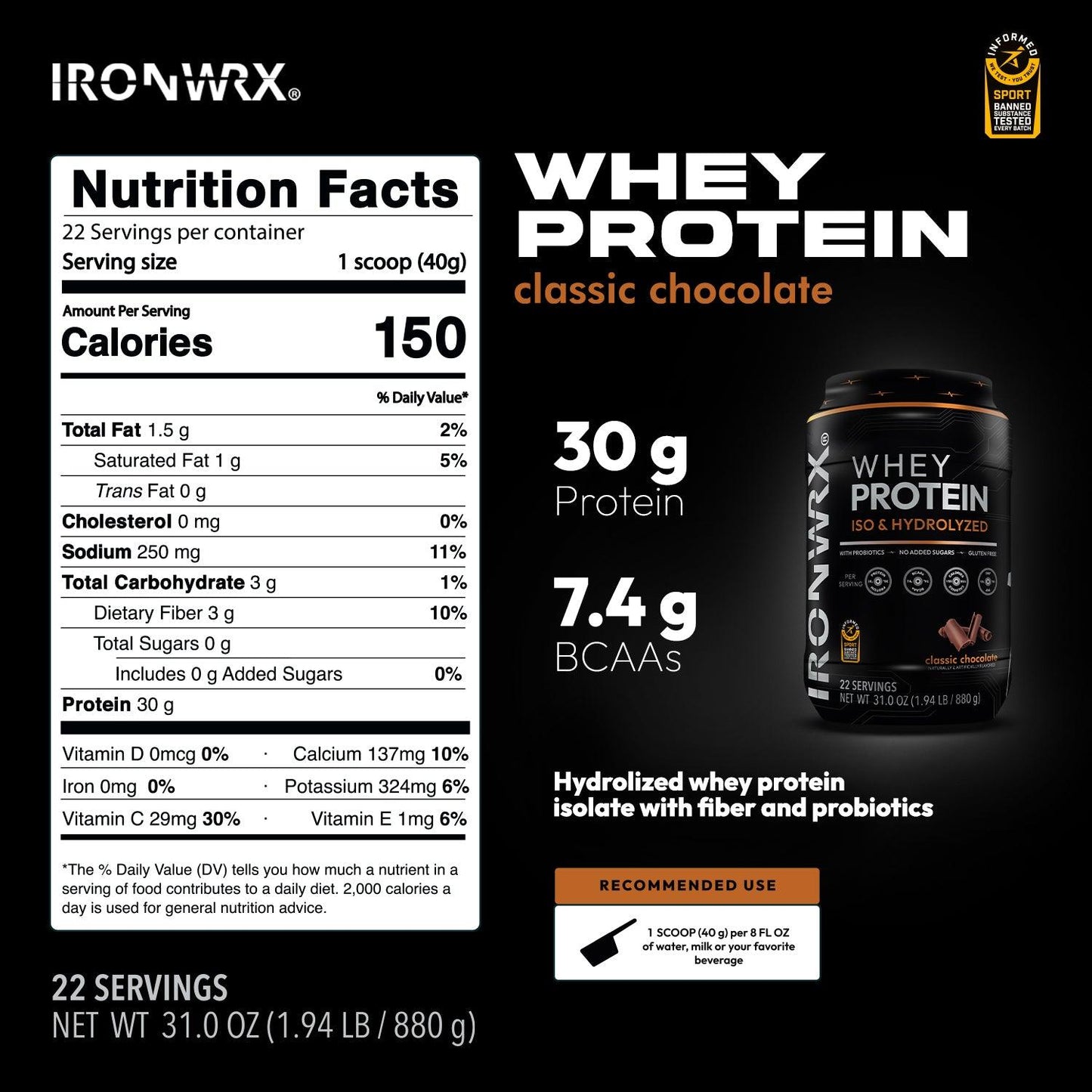
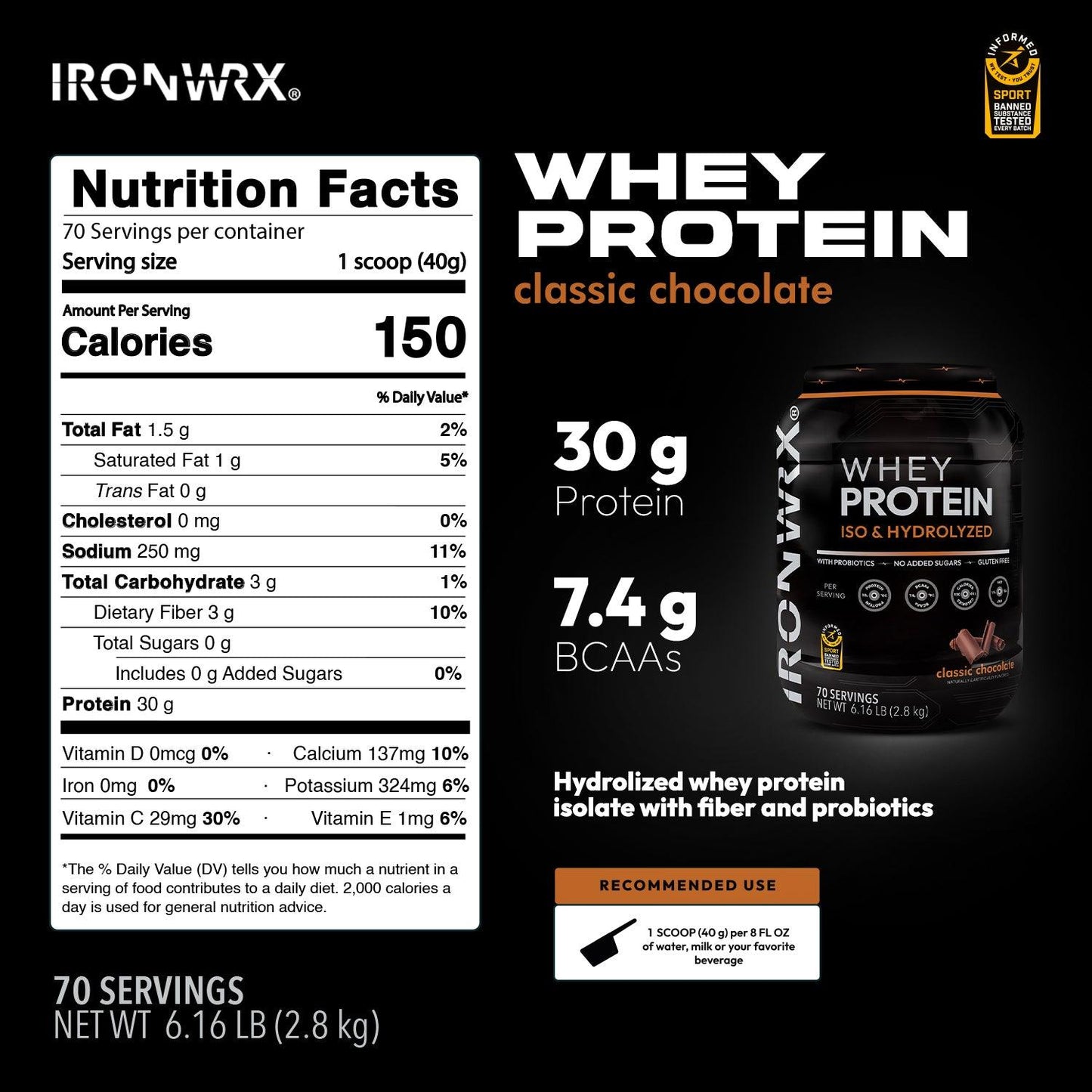
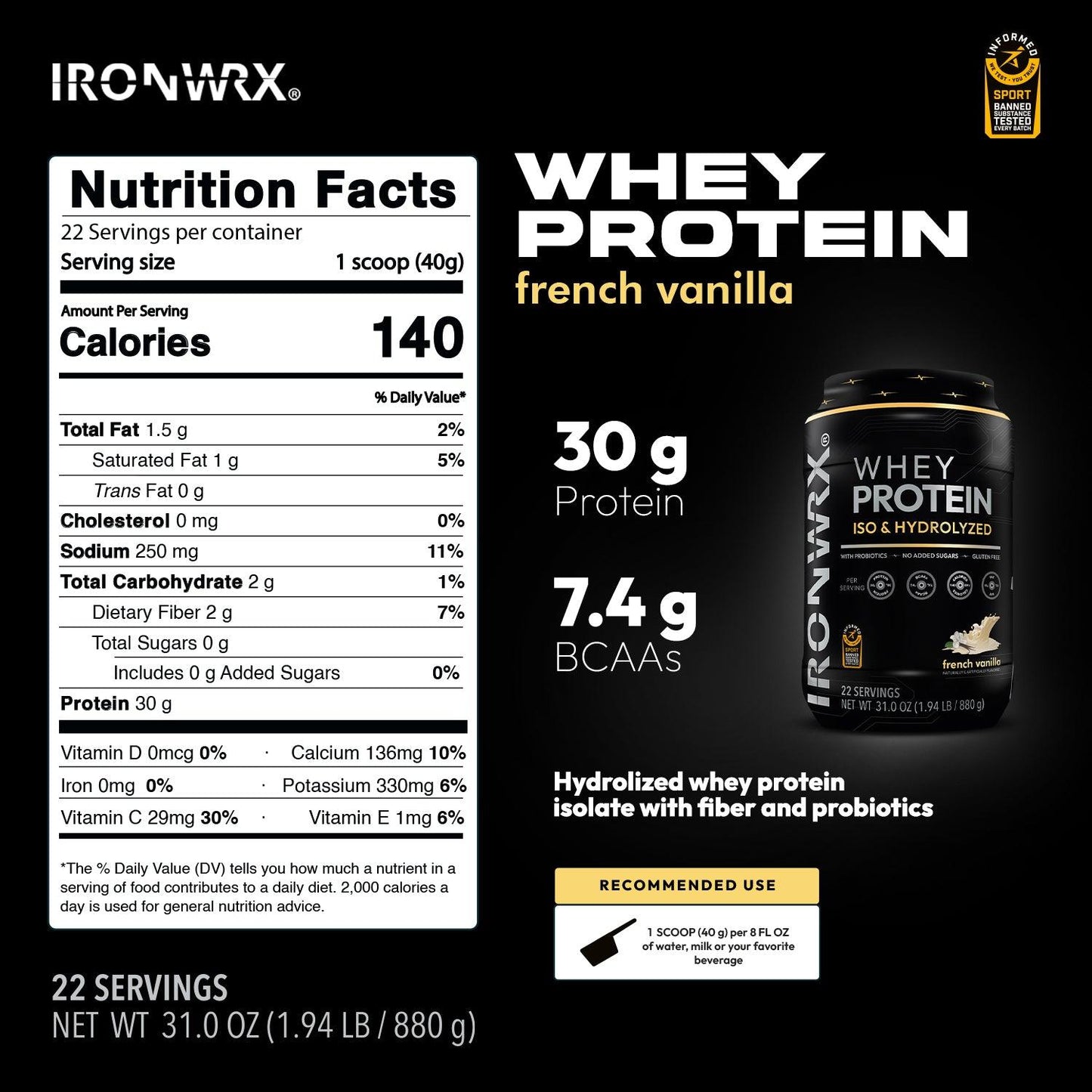
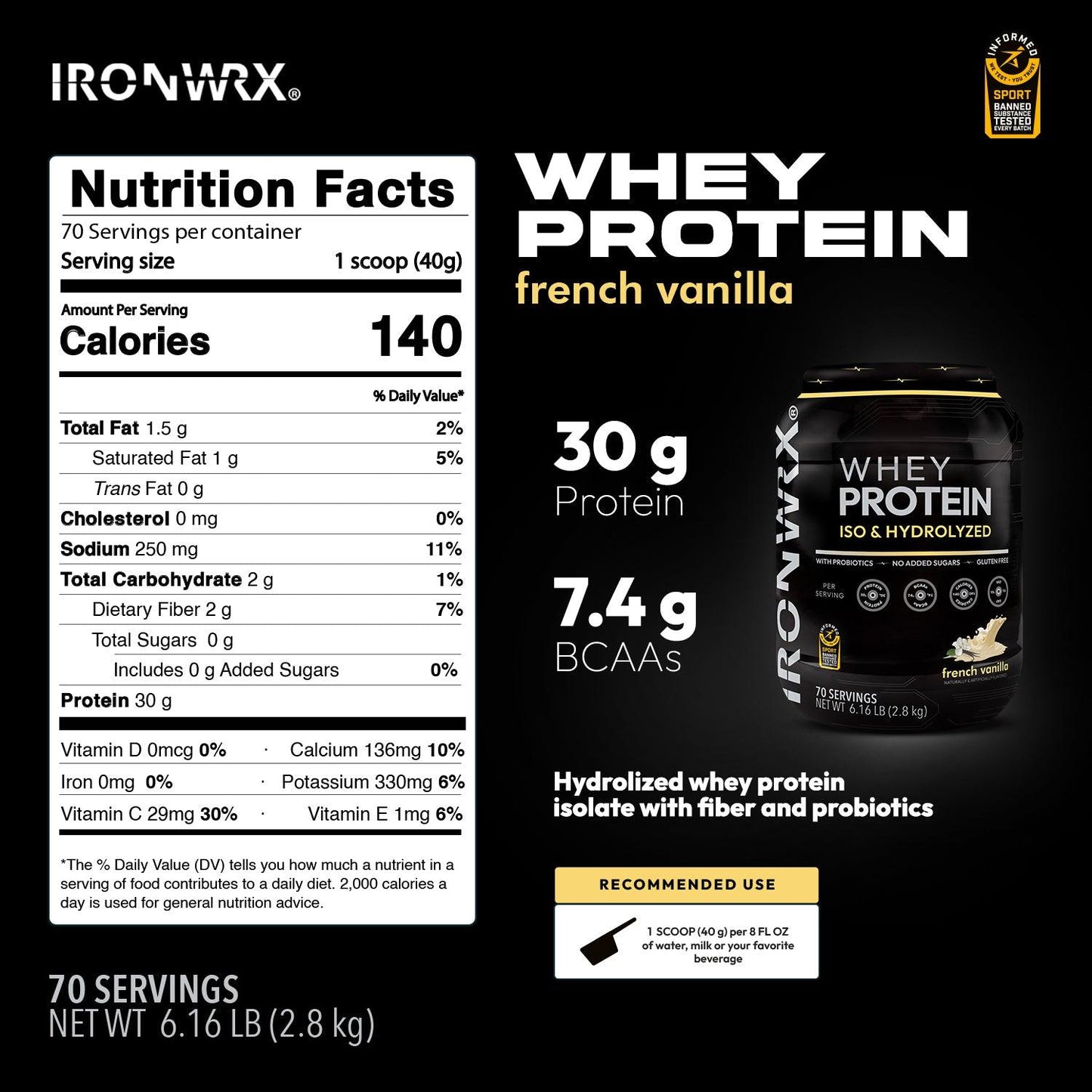
Whey Protein FAQs
What is whey protein?
Whey protein is a high-quality protein derived from milk. It's the liquid leftover after milk is curdled and strained during cheese production. Whey protein is then
processed into a powder form, making it a convenient and fast absorbing way to
boost your daily protein intake.
What are the different types of whey protein?
There are two main types of whey protein commonly found in supplements:
- Whey concentrate (WPC): This is the most common and affordable type of whey protein. It contains around 70-80% protein by weight, with some lactose and fat
- Whey isolate (WPI): This is a more refined form of whey protein, containing around 90% protein by weight. WPI is lower in lactose and fat than WPC
Additionally whey protein can be hydrolyzed. This process breaks down the protein chains into smaller peptides, making them easier and faster to digest.
What are the benefits of hydrolyzed whey protein isolate?
Whey protein offers several benefits, including:
- Muscle building and repair: Whey protein is a complete protein, containing all the essential amino acids your body needs to build and repair muscle tissue.
- Improved satiety: Protein helps you feel fuller for longer, which can aid in weight management.
- Enhanced athletic performance: Whey protein can help improve muscle recovery after exercise, leading to better performance.
Who can benefit from whey protein?
Whey protein can be beneficial for a variety of people, including:
- Athletes and bodybuilders: To support muscle growth and recovery.
- People trying to lose weight: As protein can help with satiety and manage calorie intake.
- Individuals with active lifestyles: To ensure they meet their daily protein needs.
- People recovering from injury or surgery: To support tissue repair.
Does whey protein cause bloating or gas?
Lactose intolerance can cause bloating and gas. Whey isolate is very low in lactose, so it's generally tolerated well by most people. If you have concerns about lactose intolerance, consult your doctor before using whey protein.
How much whey protein should I take?
The recommended dosage of whey protein depends on your individual needs and goals. A general rule of thumb is to consume 0.5g of protein per pound of body weight.
It's advisable to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietician to determine the optimal dosage for you based on you eating habits and lifestyle.
When should I take whey protein?
Whey protein can be consumed at various times throughout the day, depending on your goals. Some common times include:
- Post-workout: To help with muscle recovery.
- In the morning: As part of a healthy breakfast to jumpstart your metabolism.
- As a snack: To curb hunger cravings and increase satiety.
How should I store whey protein powder?
Store your whey protein powder in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat. This will help maintain its freshness and quality.
Can vegans consume whey protein?
Whey protein is derived from milk, making it unsuitable for vegans. There are plant-based protein powders available as alternatives.
I have a medical condition. Can I take whey protein?
If you have any underlying medical conditions, it's best to consult your doctor before using whey protein supplements.
What is the benefit of probiotics and fiber in my whey protein?
Whey protein itself is a great source of easily absorbed protein to aid muscle growth and repair. But whey protein powders with probiotics and fiber can offer some additional benefits:
Probiotics
Improved Digestion and Lactose Tolerance: Probiotics can help break down lactose, the sugar found in whey protein, which can be helpful for people with lactose intolerance. This can lead to less bloating, gas, and cramping.
Gut Health: Probiotics can help promote a healthy gut microbiome, which is important for overall health and immunity.
Fiber
Improved Satiety:
Fiber can help you feel fuller for longer, which can be helpful for managing weight.
Regularity: Fiber can help promote regularity and digestive health.
Nutrient Absorption:
Fiber can help slow down the digestion of whey protein, which may lead to better absorption of nutrients.
Things to Consider
Not all probiotic strains are created equal: Different strains of probiotics offer different benefits. Look for a whey protein powder that contains strains that have been shown to be effective for gut health.
Dosage matters: The amount of probiotics in a whey protein powder can vary. Look for a powder that contains at least 1 billion CFU (colony forming units) of probiotics per serving.
Fiber source: Some whey protein powders with fiber use inulin, a type of prebiotic fiber. Prebiotics help feed the good bacteria in your gut.
Overall, whey protein powder with probiotics and fiber can be a convenient way to boost your protein intake, improve your gut health, and promote overall health.
However, it is important to note that more research is needed to confirm the long-term benefits of these supplements. If you have any concerns about using whey protein powder
with probiotics and fiber, talk to your doctor.
Should I use whey protein if I am pregnant or breastfeeding?
Talk to your
doctor before taking any supplements, including whey protein, if you are
pregnant or breastfeeding.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for educational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements or making changes to your diet.
IRONWRX
100% Hydrolyzed Whey Protein Isolate – 30g Protein, 7.4g BCAAs, Easy Digestion | IRONWRX
Share